Rank the acids in order of decreasing acid strength – Understanding acid strength is crucial in chemistry, as it influences various chemical reactions and industrial processes. This article explores the concept of acid strength and provides a comprehensive guide to ranking acids in order of decreasing acid strength, discussing the factors that affect acid strength, methods used for ranking, and practical applications of these rankings.
Factors Affecting Acid Strength
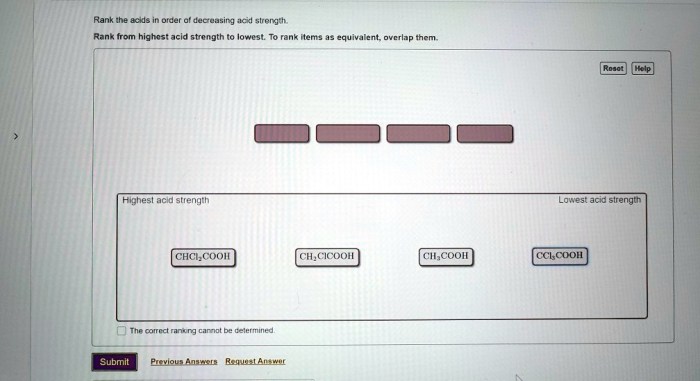
The strength of an acid is primarily determined by the following factors:
Acid Dissociation Constant (Ka)
The Ka value is a quantitative measure of the extent to which an acid dissociates in water. A higher Ka value indicates a stronger acid, as it dissociates more readily.
Molecular Structure
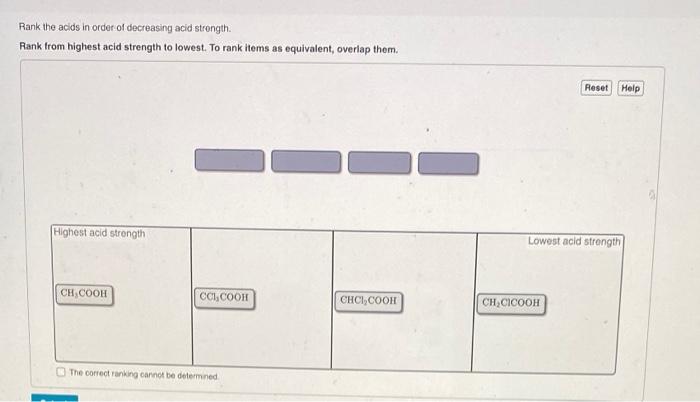
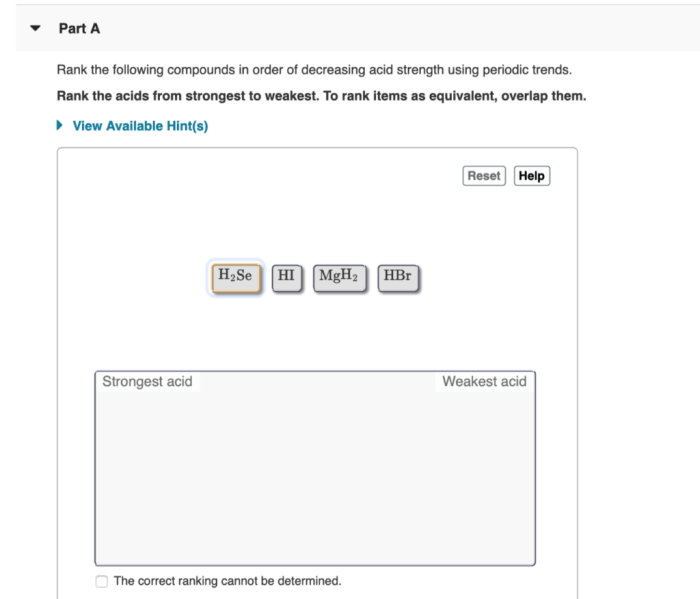
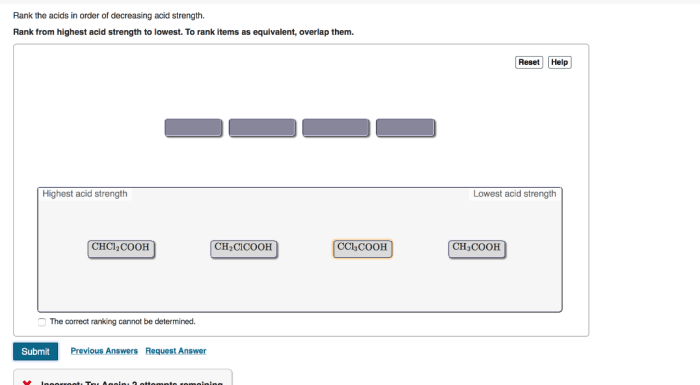
The molecular structure of an acid can influence its strength. Acids with a more electronegative central atom (e.g., N, O, F) are generally stronger than those with a less electronegative central atom (e.g., C, H).
Hybridization of the Central Atom, Rank the acids in order of decreasing acid strength
The hybridization of the central atom in an acid also affects its strength. Acids with a more sp-hybridized central atom (e.g., sp, sp2) are generally stronger than those with a less sp-hybridized central atom (e.g., sp3).
Key Questions Answered: Rank The Acids In Order Of Decreasing Acid Strength
What is the significance of ranking acids in order of decreasing acid strength?
Ranking acids helps predict chemical reactivity, design industrial processes, and understand biological systems.
What factors influence the strength of an acid?
Acid dissociation constant (Ka), molecular structure, and hybridization of the central atom are key factors.
How can acids be ranked in order of decreasing acid strength?
Methods include using Ka values, pH measurements, and titration experiments.