Embark on an enlightening journey into the captivating realm of symbiosis with our comprehensive symbiosis worksheet PDF answer key. This invaluable resource unravels the intricacies of symbiotic relationships, empowering you with a profound understanding of the intricate dance between species.
Within this meticulously crafted guide, you will discover the fundamental concepts of symbiosis, exploring the nuances of mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism. Delve into the diverse categories of symbiotic relationships, unraveling the complexities of obligate, facultative, and temporary partnerships.
Symbiosis Definitions

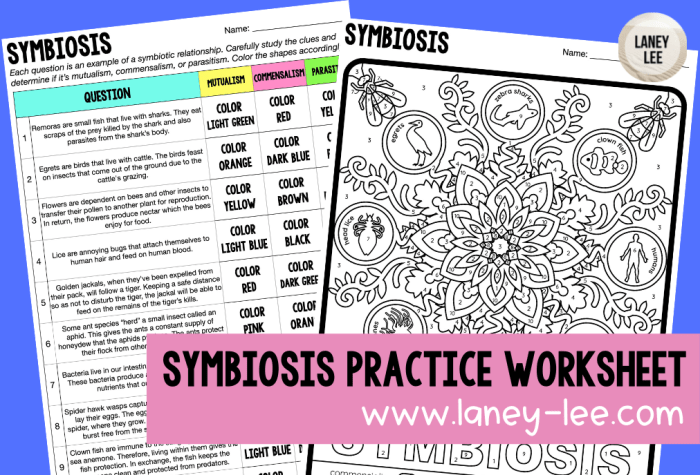
Symbiosis refers to a close and long-term biological interaction between two different species. These interactions can range from mutually beneficial to harmful for one or both partners. The three main types of symbiosis are:
- Mutualism:Both species benefit from the relationship.
- Commensalism:One species benefits while the other is neither harmed nor benefited.
- Parasitism:One species (the parasite) benefits at the expense of the other (the host).
Examples of these symbiotic relationships include:
- Mutualism:Bees and flowers (bees pollinate flowers and get nectar)
- Commensalism:Barnacles on whales (barnacles attach to whales for protection and mobility)
- Parasitism:Tapeworms in humans (tapeworms live in the human digestive tract and absorb nutrients)
Types of Symbiotic Relationships
Symbiotic relationships can be further classified based on their duration and the degree of dependence between the partners:
Obligate Symbiosis
Both species cannot survive independently of each other. Examples include:
- Lichen (a fungus and an alga)
- Mycorrhizae (a fungus and a plant root)
Facultative Symbiosis
Both species can survive independently but benefit from the relationship. Examples include:
- Bees and flowers
- Clownfish and sea anemones
Temporary Symbiosis
The interaction occurs only for a specific purpose or period. Examples include:
- Predators and prey
- Host-parasite interactions
Symbiosis in Ecosystems
Symbiotic relationships play a crucial role in ecosystems:
- Biodiversity:Symbiosis promotes species diversity by creating specialized niches and facilitating co-existence.
- Ecosystem Stability:Symbiotic relationships help maintain ecosystem balance by regulating nutrient cycling, energy flow, and population dynamics.
Examples of symbiotic relationships in ecosystems include:
- Coral reefs:Symbiosis between corals and algae provides nutrients and protection.
- Nitrogen-fixing bacteria:Symbiosis with plants helps fix atmospheric nitrogen, enriching the soil.
Benefits and Costs of Symbiosis
Symbiotic relationships can provide both benefits and costs for the partners:
Benefits
- Increased access to resources
- Protection from predators or harsh conditions
- Improved reproductive success
Costs
- Increased energy expenditure
- Competition for resources within the relationship
- Potential for exploitation or harm
The outcome of a symbiotic interaction depends on factors such as the species involved, environmental conditions, and the duration of the relationship.
Evolution of Symbiosis
Symbiotic relationships have evolved through natural selection and co-evolution:
- Natural Selection:Individuals with traits that enhance symbiotic relationships have a higher chance of survival and reproduction.
- Co-evolution:Over time, the interacting species may evolve adaptations that further optimize their symbiotic partnership.
Examples of co-evolution in symbiosis include:
- The co-evolution of flowering plants and pollinators
- The co-evolution of termites and their gut microbiota
Applications of Symbiosis
Symbiotic relationships have practical applications in various fields:
Agriculture, Symbiosis worksheet pdf answer key
- Nitrogen-fixing bacteria:Used to enhance crop yields by fixing atmospheric nitrogen.
- Mycorrhizal fungi:Improve plant growth and nutrient uptake.
Medicine
- Antibiotics:Produced by bacteria and fungi that have symbiotic relationships with other organisms.
- Probiotics:Beneficial bacteria used to improve gut health.
Biotechnology
- Biofuels:Produced using symbiotic relationships between microorganisms and plants.
- Bioremediation:Using symbiotic microorganisms to clean up environmental pollutants.
FAQ Summary: Symbiosis Worksheet Pdf Answer Key
What is the difference between mutualism and commensalism?
In mutualism, both species benefit from the relationship, while in commensalism, one species benefits while the other is unaffected.
How does symbiosis contribute to ecosystem stability?
Symbiosis enhances resource utilization, nutrient cycling, and resilience to environmental disturbances, promoting ecosystem stability.
What are the evolutionary mechanisms driving symbiosis?
Natural selection and co-evolution shape symbiotic relationships, favoring partnerships that enhance survival and reproductive success.
