Atomic structure worksheet answers chemistry sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. This comprehensive guide delves into the fundamental principles of atomic structure, electron configuration, periodic trends, chemical bonding, and the applications of atomic structure in various fields, providing a thorough understanding of the building blocks of matter.
The content of the second paragraph that provides descriptive and clear information about the topic
Atomic Structure Basics
Atomic structure is the fundamental framework of matter, defining the structure and properties of atoms. It involves the study of the subatomic particles that make up atoms, their arrangement, and their interactions.
Atoms are composed of three fundamental particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons reside in the atom’s nucleus, while electrons orbit around the nucleus in specific energy levels.
The atomic number of an atom, represented by the symbol Z, is the number of protons in the nucleus. It determines the element to which the atom belongs. The mass number, denoted by the symbol A, is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
Isotopes of the same element have the same atomic number but different mass numbers.
The number of electrons in an atom is equal to the number of protons, making the atom electrically neutral. Electrons are arranged in energy levels, or shells, around the nucleus. The first shell can hold up to 2 electrons, the second shell up to 8 electrons, and so on.
Electron Configuration
Electron configuration refers to the distribution of electrons in the energy levels or orbitals around the nucleus. It is crucial for understanding the chemical properties of an element.
The Aufbau principle states that electrons occupy the lowest energy orbitals available before moving to higher energy levels. This principle helps predict the electron configuration of an atom.
| Element | Symbol | Atomic Number | Electron Configuration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | H | 1 | 1s1 |
| Helium | He | 2 | 1s2 |
| Lithium | Li | 3 | 1s2 2s1 |
| Beryllium | Be | 4 | 1s2 2s2 |
| Boron | B | 5 | 1s2 2s2 2p1 |
| Carbon | C | 6 | 1s2 2s2 2p2 |
| Nitrogen | N | 7 | 1s2 2s2 2p3 |
| Oxygen | O | 8 | 1s2 2s2 2p4 |
| Fluorine | F | 9 | 1s2 2s2 2p5 |
| Neon | Ne | 10 | 1s2 2s2 2p6 |
Periodic Trends

Periodic trends are regular variations in the properties of elements as their atomic number increases. These trends can be observed in the periodic table and provide valuable insights into the behavior of elements.
Some notable periodic trends include:
- Atomic Radius:Generally decreases across a period from left to right and increases down a group.
- Ionization Energy:Generally increases across a period from left to right and decreases down a group.
- Electronegativity:Generally increases across a period from left to right and decreases down a group.
Understanding these trends helps predict the chemical properties of elements and allows for the classification of elements into groups and periods.
Chemical Bonding: Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers Chemistry
Chemical bonding refers to the interactions between atoms that result in the formation of molecules or compounds. There are three main types of chemical bonds:
- Ionic Bonding:Involves the transfer of electrons from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of positively and negatively charged ions.
- Covalent Bonding:Involves the sharing of electrons between atoms, resulting in the formation of a covalent bond.
- Metallic Bonding:Involves the sharing of electrons in a sea of mobile electrons, resulting in the formation of a metallic bond.
The type of chemical bond formed depends on the electronegativity and atomic structure of the atoms involved.
Applications of Atomic Structure
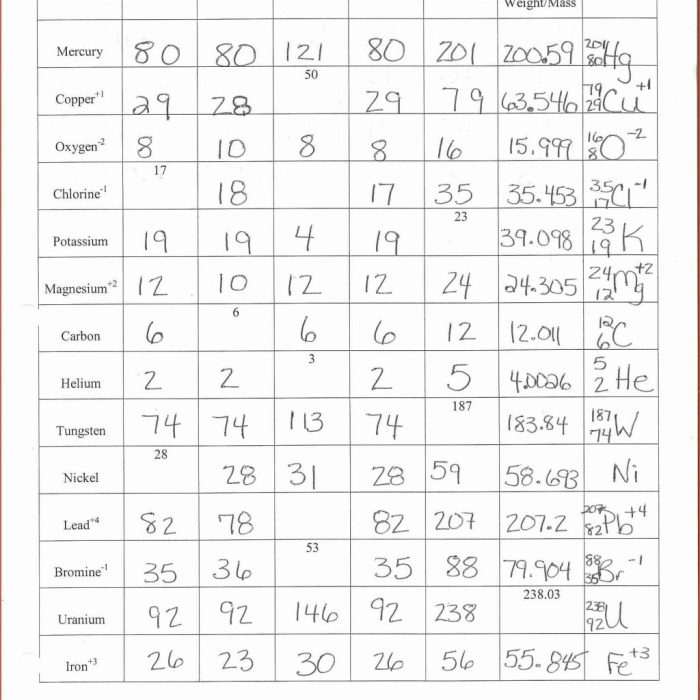
Understanding atomic structure has numerous applications in various fields:
- Chemistry:Predicts the chemical properties of elements and aids in the design of new materials.
- Materials Science:Helps design and develop materials with specific properties for applications in electronics, energy storage, and more.
- Medicine:Contributes to the development of new drugs and treatments by understanding the interactions between atoms and biological molecules.
The study of atomic structure continues to drive scientific advancements and technological innovations.
FAQ Resource
What is atomic structure?
Atomic structure refers to the arrangement and properties of the subatomic particles that make up an atom, including protons, neutrons, and electrons.
What is electron configuration?
Electron configuration describes the distribution of electrons in different energy levels or orbitals around the nucleus of an atom.
What are periodic trends?
Periodic trends are the规律的变化in the properties of elements as their atomic number increases, as observed in the periodic table.
What is chemical bonding?
Chemical bonding refers to the forces that hold atoms together to form molecules and compounds.
What are the applications of atomic structure?
Atomic structure has wide-ranging applications in fields such as chemistry, materials science, medicine, and nanotechnology.