The dichotomous key to the animal kingdom stands as an indispensable tool for scientists and naturalists, enabling the systematic identification and classification of animals. This comprehensive guide explores the concept, structure, and applications of dichotomous keys, highlighting their significance in scientific research and conservation efforts.
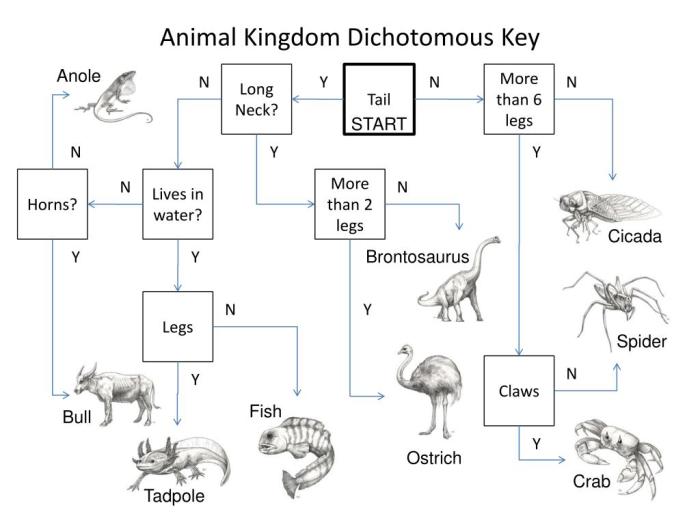
Dichotomous keys present a series of paired statements or couplets, each leading to a subsequent couplet or to the identification of a specific animal group. This binary approach simplifies the identification process, allowing users to narrow down possibilities based on observable characteristics.
Dichotomous Key Definition
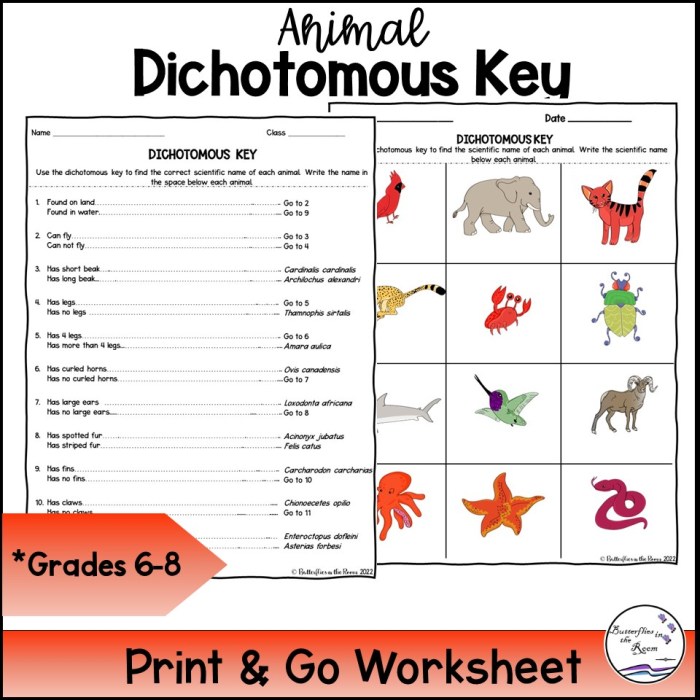
A dichotomous key is a taxonomic tool that helps identify and classify organisms by presenting a series of paired statements or questions, known as couplets. Each couplet provides two contrasting characteristics, and the user selects the statement that best describes the specimen in question.
Dichotomous keys are valuable in various fields, including biology, ecology, and conservation. They offer a systematic and efficient way to identify organisms, making them essential for research, education, and practical applications.
Structure and Format, Dichotomous key to the animal kingdom
Dichotomous keys typically follow a consistent structure:
- Lead statement:Introduces the key and provides general information about the group of organisms being identified.
- Couplets:A series of paired statements that present contrasting characteristics. Each couplet is numbered, and the user selects the statement that best describes the specimen.
- Indentations:Indentations are used to organize the couplets and indicate the hierarchical relationship between statements.
- Lead to:The statements in a couplet lead to subsequent couplets or to a terminal statement that identifies the organism.
- Terminal statements:These statements provide the identification of the organism and may include additional information such as the scientific name, common name, or habitat.
Application in Animal Kingdom
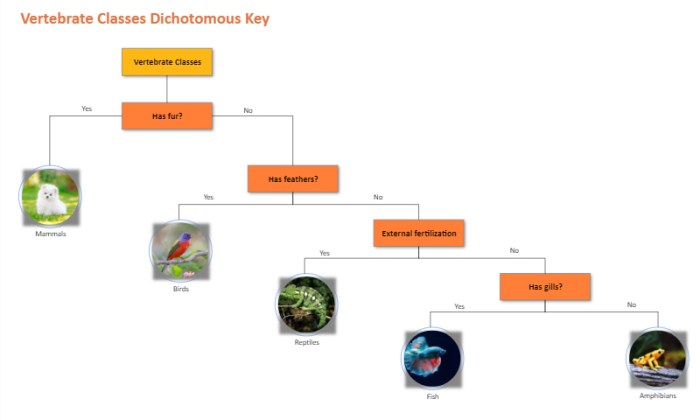
Dichotomous keys play a crucial role in classifying animals. They provide a standardized method for identifying and grouping organisms based on their morphological, behavioral, and ecological characteristics.
For example, a dichotomous key can be used to identify different species of birds based on their beak shape, wingspan, and habitat. By following the key’s couplets, users can narrow down the possibilities and determine the correct identification.
Dichotomous keys are also essential in scientific research and conservation efforts. They facilitate the accurate identification of species, which is critical for population studies, biodiversity assessments, and conservation planning.
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages of Dichotomous Keys:
- Systematic and efficient:Provides a step-by-step approach to identification, making it easy to follow and use.
- Standardized:Ensures consistency in identification across different users and eliminates subjectivity.
- Educational value:Helps users learn about the characteristics and diversity of organisms.
Limitations of Dichotomous Keys:
- May not be comprehensive:Keys may not include all possible variations within a group of organisms.
- Relies on accurate observations:Misidentification can occur if the user does not correctly observe the specimen’s characteristics.
- Can be time-consuming:For large and diverse groups of organisms, using a dichotomous key can be a lengthy process.
Creating a Dichotomous Key
Creating a dichotomous key involves the following steps:
- Define the purpose and scope:Determine the group of organisms to be identified and the characteristics to be used.
- Gather data:Collect information about the organisms, including their morphological, behavioral, and ecological characteristics.
- Organize the data:Group the characteristics into contrasting pairs that can be used to differentiate between organisms.
- Write the lead statement:Introduce the key and provide general information about the group of organisms.
- Write the couplets:Formulate clear and concise couplets that present the contrasting characteristics.
- Indicate the lead to:Specify the subsequent couplets or terminal statements that correspond to each statement in a couplet.
- Write the terminal statements:Provide the identification of the organism and any additional information.
- Test and refine:Use the key to identify a sample of organisms and make necessary adjustments to improve its accuracy and efficiency.
FAQ: Dichotomous Key To The Animal Kingdom
What is the purpose of a dichotomous key?
A dichotomous key is designed to assist in the identification of organisms by presenting a series of paired statements or couplets. Each couplet leads to another couplet or to the identification of a specific organism based on its observable characteristics.
How are dichotomous keys structured?
Dichotomous keys typically follow a hierarchical structure, with each couplet presenting two contrasting statements. Each statement leads to another couplet or to the identification of a specific animal group.
What are the advantages of using dichotomous keys?
Dichotomous keys offer several advantages, including their simplicity, ease of use, and ability to identify organisms based on observable characteristics. They are also a valuable tool for scientific research and conservation efforts.