Quiz 2 relations and functions – Embark on an exciting journey with Quiz 2: Relations and Functions, where we delve into the fascinating realm of mathematical connections. Discover the essence of relations and functions, explore their diverse types, and witness their transformative power in real-world applications.
From equivalence relations to exponential functions, this quiz promises an engaging exploration of the concepts that underpin our understanding of the world around us.
Relations and Functions: Quiz 2 Relations And Functions
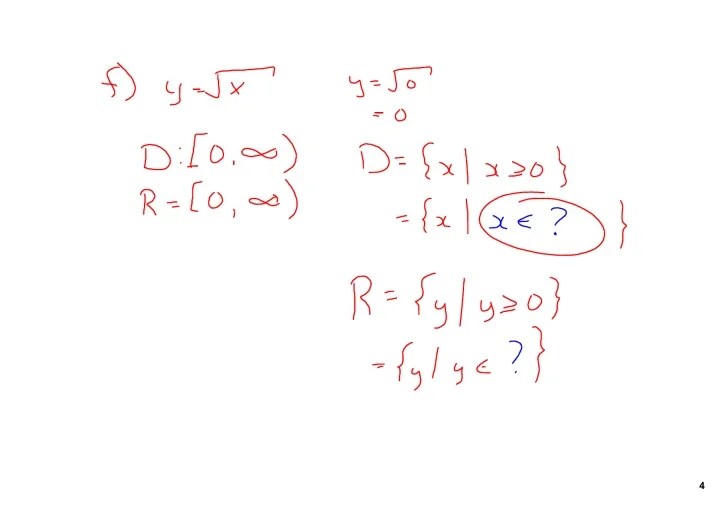
In mathematics, a relation is a set of ordered pairs. Each ordered pair consists of two elements, called the first element and the second element. A function is a special type of relation where each element in the domain is paired with exactly one element in the range.
Examples of Relations and Functions
- The relation (1, 2), (3, 4), (5, 6) is a relation because it is a set of ordered pairs.
- The function (1, 2), (3, 4), (5, 6) is a function because each element in the domain is paired with exactly one element in the range.
- The relation (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4) is not a function because the element 1 in the domain is paired with multiple elements in the range.
Domain and Range of a Function
The domain of a function is the set of all first elements in the ordered pairs. The range of a function is the set of all second elements in the ordered pairs.
For example, the domain of the function (1, 2), (3, 4), (5, 6) is 1, 3, 5. The range of the function (1, 2), (3, 4), (5, 6) is 2, 4, 6.
Types of Relations and Functions
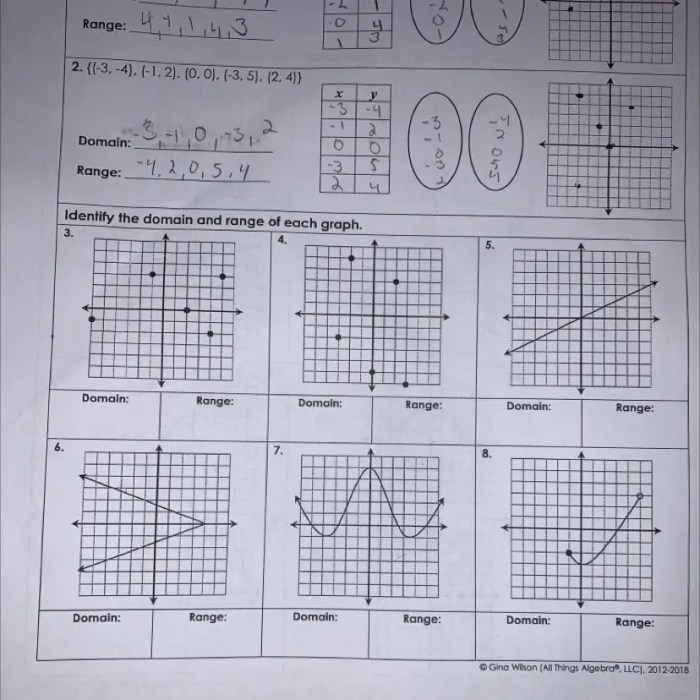
Relations and functions are mathematical concepts that describe how two sets of elements are connected. In this section, we will explore different types of relations and functions, their properties, and how they are classified.
After a quick break, let’s dive back into Quiz 2 on relations and functions. In case you need a bit of a refresher, the last of the mohicans costumes can serve as a fun visual aid. The intricate designs and patterns on these costumes can help us understand the concept of domain and range, and how different inputs can produce different outputs.
So, let’s get back to the quiz and see how well you can apply these concepts.
Types of Relations
Relations are sets of ordered pairs that connect elements from two sets. Different types of relations exist, each with specific properties:
- Equivalence Relations:These relations are reflexive, symmetric, and transitive. In other words, for any elements a, b, and c in the set, if aRb, then bRa (reflexivity), if aRb, then bRa (symmetry), and if aRb and bRc, then aRc (transitivity).
- Order Relations:These relations establish an ordering among the elements of a set. They can be either total or partial. A total order relation allows for any two elements to be compared, while a partial order relation may not allow for all elements to be compared.
Types of Functions
Functions are special types of relations that satisfy the condition that each element in the domain is mapped to exactly one element in the range. Functions can be classified into various types based on their properties:
- Linear Functions:These functions have a constant rate of change and can be represented by the equation y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept.
- Quadratic Functions:These functions have a parabolic shape and can be represented by the equation y = ax^2 + bx + c, where a, b, and c are constants.
- Exponential Functions:These functions increase or decrease rapidly and can be represented by the equation y = a^x, where a is a constant.
Operations on Relations and Functions
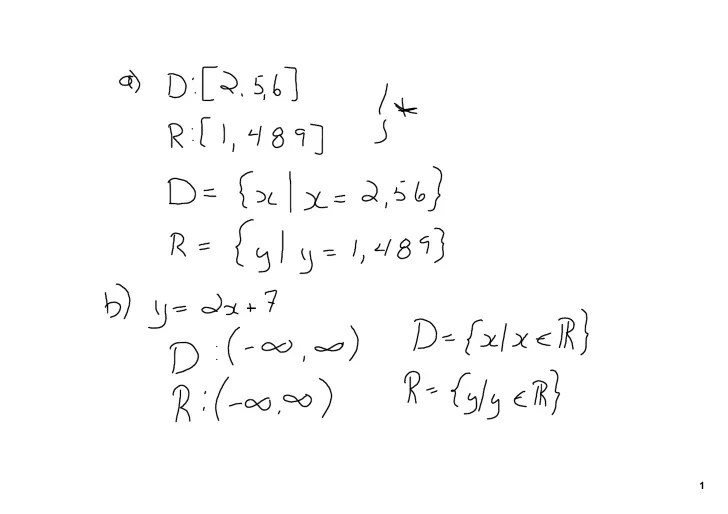
Operations on relations and functions allow us to combine or transform them to create new mathematical objects. These operations preserve certain properties of the original relations or functions, providing insights into their behavior.
Operations on Relations
- Union:The union of two relations R and S, denoted as R ∪ S, is a new relation that contains all ordered pairs that belong to either R or S.
- Intersection:The intersection of two relations R and S, denoted as R ∩ S, is a new relation that contains all ordered pairs that belong to both R and S.
- Composition:The composition of two relations R and S, denoted as R ∘ S, is a new relation that contains all ordered pairs (a, c) such that there exists an element b such that (a, b) ∈ R and (b, c) ∈ S.
Operations on Functions
- Addition:The sum of two functions f and g, denoted as f + g, is a new function whose value at each input x is f(x) + g(x).
- Subtraction:The difference of two functions f and g, denoted as f – g, is a new function whose value at each input x is f(x) – g(x).
- Multiplication:The product of two functions f and g, denoted as f · g, is a new function whose value at each input x is f(x) · g(x).
Properties of Resulting Relations and Functions
The properties of the resulting relations and functions depend on the specific operations performed. However, some general properties include:
- Closure:If the original relations or functions are closed, the resulting relation or function is also closed under the operation.
- Associativity:The union and intersection operations are associative, meaning (R ∪ S) ∪ T = R ∪ (S ∪ T) and (R ∩ S) ∩ T = R ∩ (S ∩ T).
- Commutativity:The union and intersection operations are commutative, meaning R ∪ S = S ∪ R and R ∩ S = S ∩ R.
- Identity element:The empty relation is the identity element for the union operation, and the universal relation is the identity element for the intersection operation.
Applications of Relations and Functions
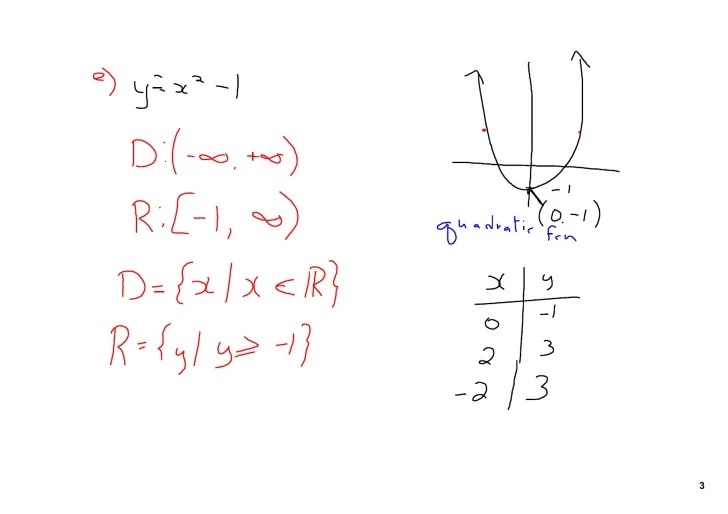
Relations and functions find extensive applications in various fields, including mathematics, science, and engineering. They provide a powerful tool to model and solve real-world problems.
Applications in Mathematics
In mathematics, relations and functions are used to study concepts such as:
- Graph theory: Representing relationships between objects using graphs.
- Number theory: Investigating properties of numbers and their relationships.
- Algebra: Modeling algebraic structures and their properties.
Applications in Science
In science, relations and functions are used to model:
- Physics: Describing relationships between physical quantities, such as force, velocity, and acceleration.
li>Chemistry: Modeling chemical reactions and the behavior of molecules.
li>Biology: Representing biological processes, such as population growth and genetic inheritance.
Applications in Engineering, Quiz 2 relations and functions
In engineering, relations and functions are used to:
- Design and analysis: Modeling engineering systems and analyzing their behavior.
- Control systems: Designing feedback systems to regulate and control processes.
- Optimization: Finding optimal solutions to engineering problems.
Detailed FAQs
What is the key difference between a relation and a function?
A relation pairs elements from two sets, while a function assigns each element from one set to exactly one element in another set.
Can you explain the concept of the domain and range of a function?
The domain is the set of all possible input values for a function, while the range is the set of all possible output values.
What are some common types of functions?
Linear, quadratic, exponential, and trigonometric functions are among the most commonly encountered types of functions.