Unveiling the remarkable tale of Volta do Mar AP World History, this exploration invites you on a journey through groundbreaking discoveries, cultural encounters, and the profound impact on the world’s trajectory.
As Portuguese explorers embarked on their epic voyages, they not only rounded the Cape of Good Hope but also reshaped global trade routes, ignited cultural exchange, and fueled technological advancements that would forever alter the course of history.
Historical Context: Volta Do Mar Ap World History
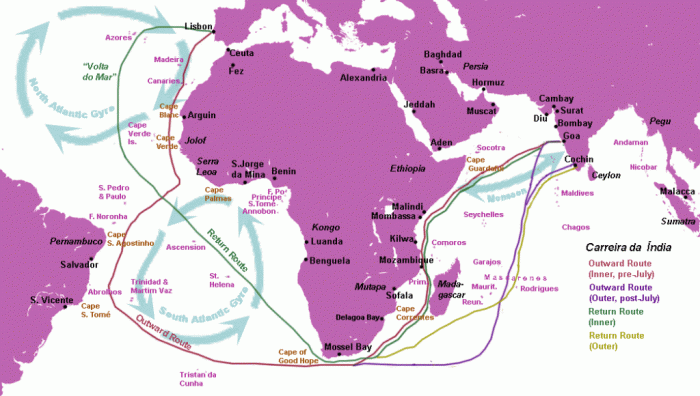
The Volta do Mar, meaning “Turn of the Sea,” was a significant milestone in Portuguese exploration. It marked the moment when Portuguese sailors rounded the southern tip of Africa, opening up a sea route to the Indian Ocean and Asia.
Volta do mar, a key concept in AP World History, refers to the period of European exploration and colonization. During this time, Europeans ventured beyond their borders, leading to significant cultural exchanges. Similarly, in the realm of faith, the concept of the six pillars of iman plays a pivotal role.
These pillars, outlined here , form the foundation of Islamic belief and guide Muslims in their daily lives. As we delve deeper into volta do mar, it’s essential to recognize the profound impact that religious beliefs had on the motivations and experiences of explorers.
The Portuguese voyages were motivated by a desire to find a new route to the East, bypassing the control of the Ottoman Empire over the traditional overland trade routes. They were also driven by a spirit of adventure and a desire to expand their knowledge of the world.
Impact on European Knowledge
The Volta do Mar had a profound impact on European knowledge of the world. It proved that the world was round, not flat as previously believed. It also expanded European knowledge of the geography of Africa and Asia, and opened up new possibilities for trade and exploration.
Exploration and Discovery

The European Age of Exploration was marked by a series of expeditions that sought to discover new trade routes and lands. One of the most significant of these expeditions was led by the Portuguese explorer Vasco da Gama.
Vasco da Gama’s Expedition
In 1497, Vasco da Gama set out from Lisbon with four ships. His goal was to find a sea route to India, which was then a major source of spices and other valuable goods.
The voyage was long and arduous. The ships had to battle storms, scurvy, and other challenges. But in 1498, da Gama and his crew finally rounded the Cape of Good Hope, the southernmost point of Africa.
From there, da Gama sailed across the Indian Ocean and reached the Malabar Coast of India in May 1498. He was the first European to sail around Africa and reach India by sea.
Importance of the Discovery
The discovery of the sea route to India was a major turning point in world history. It opened up a new trade route between Europe and Asia, and it led to the establishment of European colonies in India and other parts of Asia.
The discovery of the sea route to India also had a profound impact on the economy of Europe. The influx of spices and other goods from Asia led to a period of economic growth and prosperity.
Impact on Global Trade
The Volta do Mar revolutionized global trade routes, connecting Europe and Asia like never before. The Portuguese established trading posts along the African coast and in Asia, facilitating the exchange of goods between these regions.
Establishment of Trading Posts, Volta do mar ap world history
Portuguese traders established trading posts in strategic locations, such as Goa in India and Malacca in Southeast Asia. These posts served as hubs for trade, where European goods were exchanged for Asian spices, textiles, and other exotic commodities.
Exchange of Goods
The Volta do Mar enabled the exchange of a wide range of goods between Europe and Asia. Europeans exported manufactured goods, weapons, and textiles to Asia, while importing spices, porcelain, and silk from the East.
Portuguese Control of the Spice Trade
The Portuguese gained control of the lucrative spice trade, which had previously been dominated by Arab and Indian merchants. This monopoly gave Portugal immense economic and political power, as spices were highly sought after in Europe.
Cultural Exchange and Encounters
The Volta do Mar voyages initiated a period of extensive cultural exchange between Portuguese explorers and the diverse peoples they encountered along the African and Asian coasts. These encounters had a profound impact on both the Europeans and the local populations, leading to the spread of new ideas, technologies, and religious beliefs.
One of the most significant cultural exchanges was the introduction of firearms and other European technologies to Africa and Asia. These weapons gave the Portuguese a military advantage over local rulers, facilitating their conquest and colonization of new territories. In turn, the Portuguese adopted new agricultural techniques and crops from the regions they visited, such as sugarcane and maize, which they introduced to their own colonies in the Americas.
Impact on Christianity and European Influence
The Volta do Mar also played a crucial role in the spread of Christianity and European influence around the world. Portuguese missionaries accompanied the explorers on their voyages, establishing churches and converting local populations to Catholicism. The Portuguese also established trading posts and forts along the coasts, which became centers of European commerce and cultural exchange.
The arrival of the Portuguese in Asia had a particularly profound impact on the region. The Portuguese introduced new technologies, such as the astrolabe and the caravel, which revolutionized navigation and trade. They also established a network of trading posts and forts, which gave them control over the lucrative spice trade between Asia and Europe.
The Volta do Mar voyages marked the beginning of a new era of global exploration and cultural exchange. The Portuguese explorers’ encounters with the peoples of Africa and Asia had a profound impact on both the Europeans and the local populations, shaping the course of world history for centuries to come.
Technological Advancements
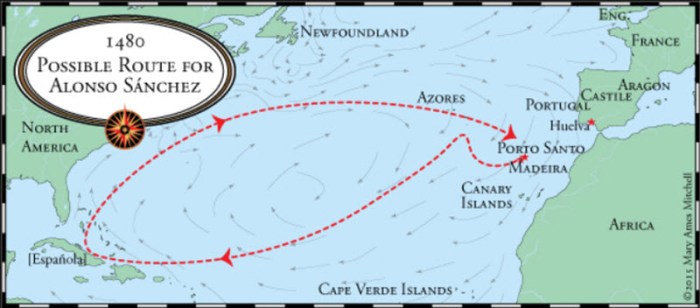
The Volta do Mar, a significant maritime expedition, was made possible by several key technological advancements that revolutionized shipbuilding, navigation, and cartography.Improvements in shipbuilding techniques led to the development of larger and more durable ships, capable of withstanding the treacherous ocean conditions.
These ships featured advanced hull designs, multiple masts and sails, and improved steering mechanisms.In the realm of navigation, the invention of the astrolabe and the quadrant enabled sailors to accurately determine their latitude and longitude. This newfound precision allowed them to chart their course more effectively and avoid getting lost at sea.Advancements
in cartography also played a crucial role. The development of more accurate maps and charts provided sailors with a better understanding of the world’s geography and coastlines, making it easier to plan their voyages and avoid potential hazards.
Development of New Instruments and Techniques
Beyond the aforementioned advancements, the Volta do Mar also benefited from the development of new instruments and techniques. The compass, first introduced by the Chinese, provided sailors with a reliable way to determine their direction even in cloudy or foggy conditions.
The use of lead lines allowed them to measure the depth of the water, helping them avoid shallow areas and potential shipwrecks.
Legacy and Impact
The Volta do Mar had a profound and lasting impact on world history, shaping the course of global trade, exploration, and cultural exchange. It marked the beginning of a new era of European expansion and dominance, leading to the establishment of global trade networks and the rise of European colonialism.
Establishment of Global Trade Networks
The Volta do Mar opened up new sea routes and facilitated the exchange of goods and ideas between different parts of the world. European powers established trading posts and colonies along the coasts of Africa, Asia, and the Americas, creating a global network of trade and commerce.
This led to the spread of new crops, technologies, and cultural influences, transforming the economies and societies of both Europe and the non-European world.
Rise of European Colonialism
The Volta do Mar played a crucial role in the rise of European colonialism. The ability to navigate and control the oceans gave European powers a significant advantage in terms of military and economic power. They used their naval superiority to establish colonies and exploit the resources of other continents, leading to the expansion of European empires and the displacement of indigenous populations.
Shaping the Modern World
The legacy of the Volta do Mar continues to shape the modern world. The global trade networks established during this period remain the foundation of the global economy, and the rise of European colonialism has had a lasting impact on the political and cultural landscapes of many regions.
Top FAQs
What were the primary motivations behind the Portuguese voyages?
The Portuguese sought to establish new trade routes, particularly to the lucrative spice markets of Asia, and to expand their global influence.
How did the Volta do Mar impact global trade?
It established new sea routes between Europe and Asia, leading to the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies, and transforming global trade patterns.
What were some of the key cultural encounters during the Volta do Mar?
Portuguese explorers encountered diverse cultures along their journeys, leading to exchanges of languages, religions, and customs, and the spread of European influence.